Model of the month December 2018 Grunau, Baby
Edmund Schneider, Grunau, Baby IIB
The Baby became the most popular training glider of the world. It was developed by Edmund Schneider in Grunau/Silesia, when Wolf Hirth was head of the gliding school (Hanna Reitsch learned to fly there, too).
Schneider and Hirth were closely connected. Schneider built training gliders, e.g. the ESG Grunau 9, the “Schädelspalter” (so named because a strut ran from the front wing in front of the pilot’s head to the fuselage floor). Edmund Schneider also built the Moazagotl for Wolf Hirth, an high-performance glider with gull wings, named after a recurring cloud over the Riesengebirge mountains.
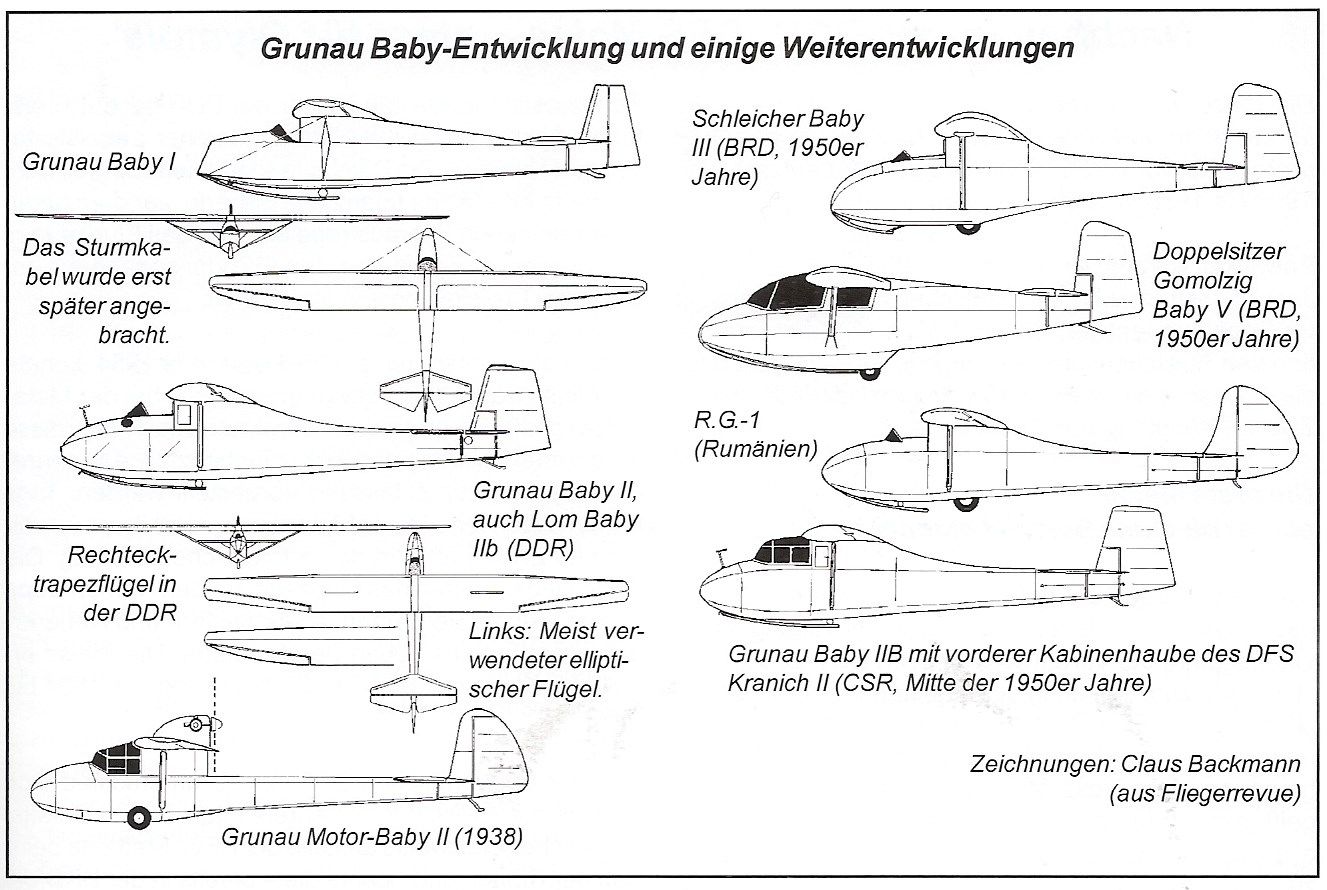
The baby I (ESG 31) of 1931 was successful, but was soon reengineered to become Baby II (winter 1931/32). When the cockpit hood was made removable (1934), it became the Baby IIA, after enlarging the ailerons and the installation of Schempp-Hirth nose-dive brakes in 1936 it became the Baby IIB.

The baby was built in large numbers industrially and privatly in glider clubs. There were replicas - with and without license - in large numbers: in France at Nord, in the UK at Slingsby, in Czechoslovakia at Zlin and after the war in the GDR at some VEBs. It was also rebuilt in West Germany, mostly by clubs. It was mass-produced by Schleicher/Rhön as Baby III (with a slightly higher hull). The exact number of Babies built is unknown, presumably more than 5000. We have an Austrian version hanging in the museum (horizontal tail rounded off).The Baby IIB served as a training and fun object for all political systems. The users had one thing in common: the joy of flying. Generations of young glider fliers learned to fly in this plane right up to high performance glider flight. It became one of the most famous aircraft. Many an aviator got his glider merit badge, the silver-C, with the Baby. Some are still flying here today, even on the dune in Rossiten/East Prussia a Baby IIB recently flew again, and on the Wasserkuppe there is one, too. Technical specifications:Wingspan 13.57 m, length 6.09 m, wing area 14.20 m², standard weight 160 kg, payload 90 kg, take-off weight 250 kg, surface load 17.60 kg/m², maximum speed 150 km/h, glide ratio 17.
(Quelle: Lemke, Frank.Dieter; Segelflugzeugbau in der DDR)
